Describe a Model of Enzyme Action
Illustration going from righ t to left. Enzymes bind to substrates so GES GES.
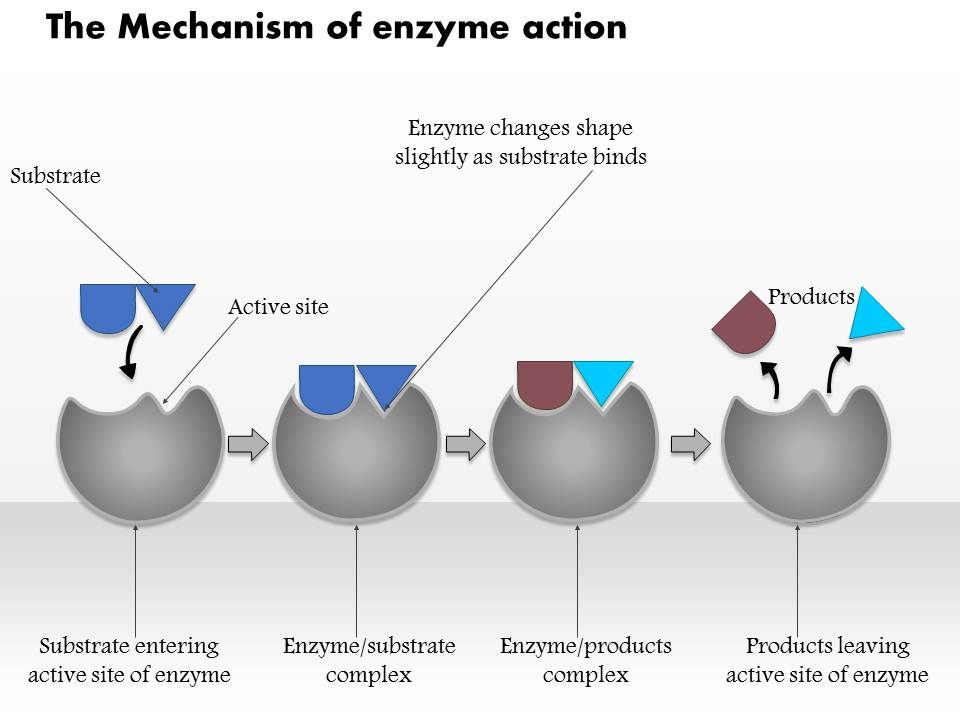
Enzymes Properties And Mechanism Of Enzyme Action Online Biology Notes
Enzyme models are used to try and describe the general mechanism that enzymes use to process substrates into new products.

. The graph shows the results of an experiment in which. As with a lock and the key that opens it the shapes must be complementary and this shape can not change. The lock and key model.
Several theories have been proposed to explain the mode of enzyme action. 1 S E E S. They discovered that the binding of a substrate often leads to a large conformational change in the enzyme as well as to changes in the structure of the substrate or substrates.
To describe the mechanism of action of enzymes to different models have been proposed. The current theory known as the induced-fit model says that enzymes can undergo a change in conformation when they bind substrate molecules and the active site has a shape complementary to that of the substrate only after the substrate is bound as shown for hexokinase in Figure 1812 The Induced-Fit Model of Enzyme Action. 2Substrates bind to the active.
This puts stress on the bonds in the substrate and so the activation energy for. The induced fit model is a way of explaining how an enzyme can aid in a biological reaction. According to this model the binding of the substrate and the enzyme takes place at the active site in a.
The substrate simply fits into the active site to form a reaction intermediate. NBPT is an enzyme inhibitor which affects the action of the urease produced by soil bacteria. According to the Induced Fit Model when substrate molecules bind to the active site of the enzyme they induce some structural changes in the active site so that it can effectively bind the substrate molecules.
Later Leonor Michaelis and Maude Menten 1913 expanded this. In a model of enzyme action the enzyme can attach only to a substrate reactant with a specific shape. In this model the enzyme molecule changes shape as the substrate molecules gets close.
1Arrows point to the active sites. Describe the induced fit model of enzyme action 2 marks 1Broken down by enzymes 2Digested 3Denatured 4To large to be absorbed. The current theory known as the induced-fit model A model that says an enzyme can undergo a conformational change when it binds substrate molecules says that enzymes can undergo a change in conformation when they bind substrate molecules and the active site has a shape complementary to that of the substrate only after the substrate is bound as shown for.
Similar to how a key has to be the correct one for a lock no reaction takes place if an incorrect substrate tries to bind. So when they bind the substrate they stress It in some way raising GES for part of the substrate and reducing ΔGESEa. Shape of active site changes as.
1 General Theory of Enzyme action Enzyme substrate complex theory. Working out the precise three-dimensional structures of numerous enzymes has enabled chemists to refine the original lock-and-key model of enzyme actions. Describe the Induced Fit Model of Enzyme Action By Da_Fatima410 16 Apr 2022 Post a Comment.
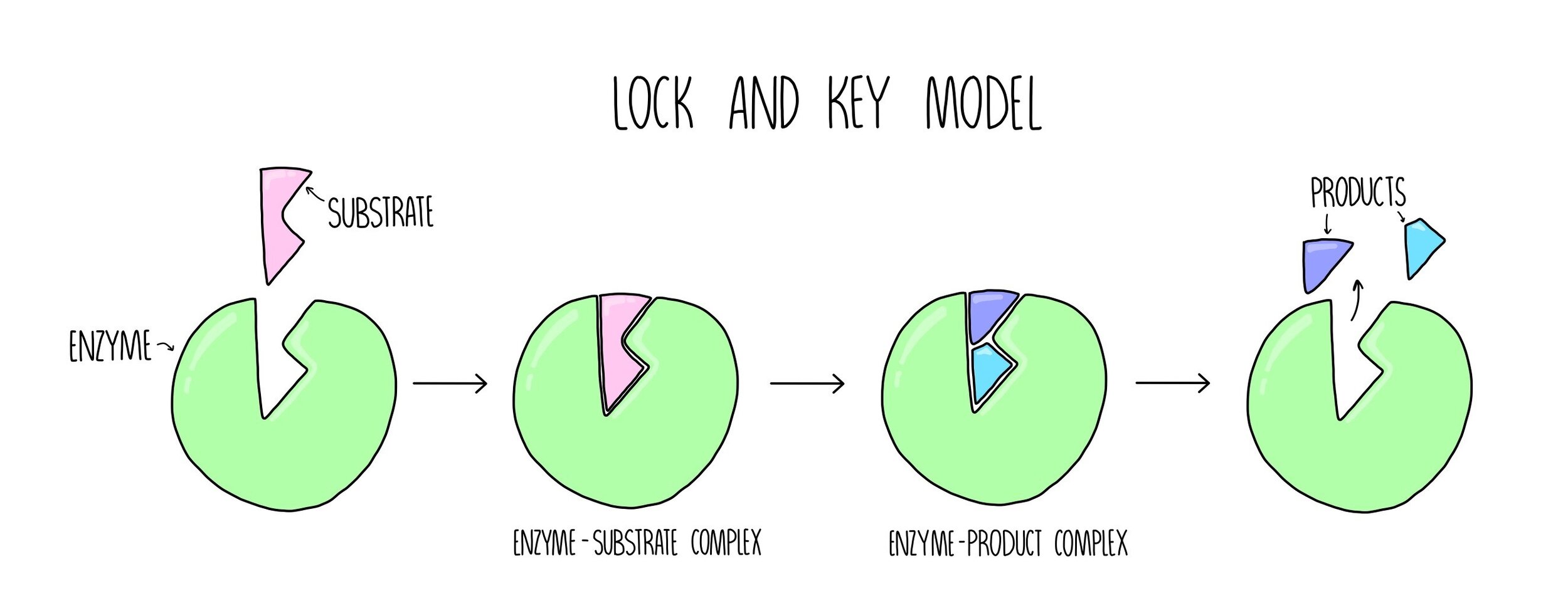
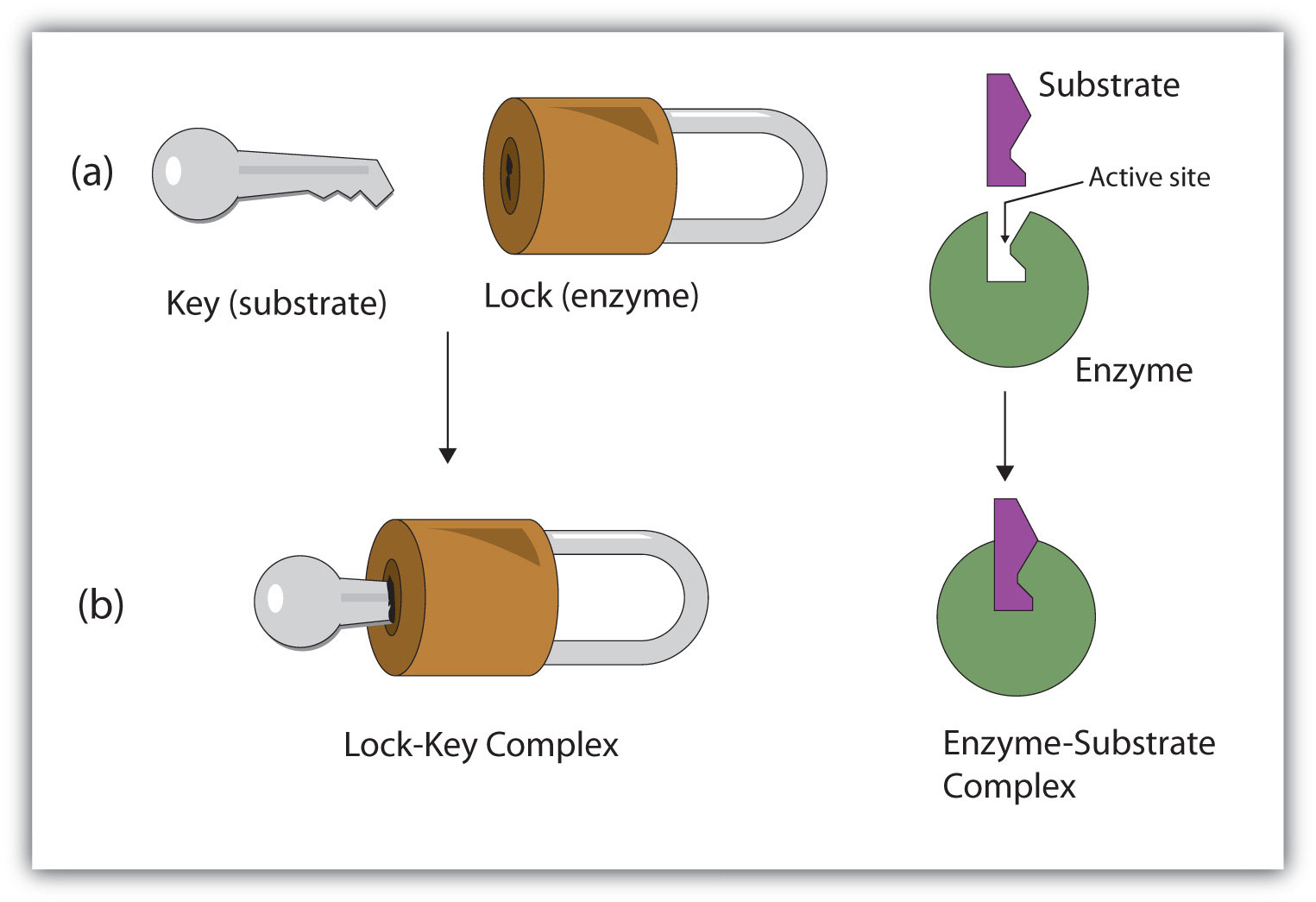
Lock and key model - theory proposed by Emil Fischer in 1894. Hydrogen bonding and other electrostatic interactions hold the enzyme and substrate together in the complex. Emil Fischer 1890 proposed a Lock and Key model to visualize substrate and enzyme interaction.
The two models to explain the actions of enzymes with substrates are the Lock and Key model Induced fit model. A more complete way of showing the effects of enzymes. The change in shape is induced by the approaching substrate molecule.
Victor Heneri 1903 first proposed that the enzyme E combines with substrate S to form enzyme-substrate ES complex as a necessary step in enzyme catalysis. There are two predominant enzyme activity models. Lock and key hypothesis.
Mechanism of enzyme action. It possesses a unique shape that complements that of the substrate. Insulin is a protein it cannot be taken orally.
The lock and key model. Induced fit looks at the active site of enzymes as being slightly more flexible and initially. According to this model as one specific key can open just a particular lock in the same manner a specific.
The Lock and Key Model. The important part of this model is that the substrate fits exactly into enzymes active site like a key into a lock. The structural features or functional groups on the enzyme that participate in these interactions are located in a cleft or pocket on the enzyme surface.
No comments for Describe the Induced Fit Model of Enzyme Action Post a Comment. Induced-fit model - an offshoot of the earlier lock-and-key model. Tap card to see definition.
2 E S P E. The lock-and-key model refers to the way in which a substrate binds to an enzymes active site. The active site of an enzyme is a specific region that receives the substrate.
The enzyme then changes and reduces the activation energy of the reaction so reactants can. 13 rows Click on the numbers below to see how the lock-and-key model of enzyme action works. In lock and key the enzyme is the lock and the substrate is the key.
When the active site of an enzyme comes into contact with the substrate the enzyme will attempt to mould itself around the substrate to form an enzyme-substrate complex. Lock And Key Model A Model For Enzyme Action Enzymes Biology Enzymes What Is A Product Share. 2 marks Click card to see definition.
There are two models for how enzyme action occurs. This model of enzyme action was proposed by Daniel E. The lock and key model was proposed by Emil Fischer in 1898 and is also known as the template model.
After catalysis the enzyme resumes. Describe the induced fit model of enzyme action. This is the simplest model to represent how an enzyme works.
This illustrations depicts the lock and key model of enzyme and substrate binding first proposed by Emile Fischer in his studies on enzymes in the nineteenth century. Before reaction active site not complementary todoes not fit substrate. States that the substrate induces a change of shape in the enzyme.
However if all they did was to bind then Ea ΔGES for the reaction would not be reduced.
Enzymes A Level The Science Hive

Enzymes Each Enzyme Lowers The Activation Energy Of The Reaction It Catalyses The Induced Fit Model Of Enzyme Action The Properties Of An Enzyme Relate Ppt Download

0 Response to "Describe a Model of Enzyme Action"
Post a Comment